When a Search Returns __________, You Can View the Results as a List.
Basic searches and search results
In this section, you create searches that retrieve events from the index.
The data for this tutorial is for the Buttercup Games online shop. The store sells games and other related items, such every bit t-shirts. In this tutorial, you volition primarily search the Apache web access logs, and correlate the access logs with the vendor sales logs.
Prerequisite
Complete the steps, Upload the tutorial data, in Office 2.
Using the Search Assistant
The Search Assistant is a feature in the Search app that appears equally you type your search criteria. The Search Assistant is like autocomplete, but so much more than.
- Click Search in the App bar to get-go a new search.
- Blazon
buttercupin the Search bar.
When you type a few letters into the Search bar, the Search Assistant shows you terms in your data that match the letters that you type in. - Click Search in the App bar to get-go a new search.
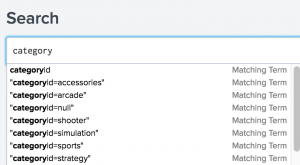
- Type
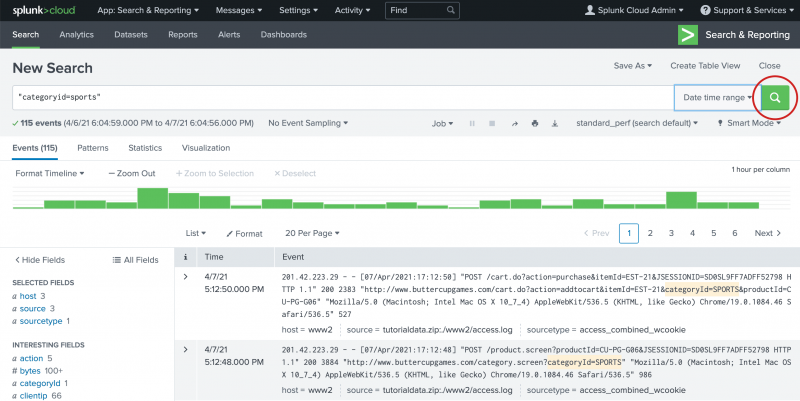
categoryin the Search bar. The terms that you see are in the tutorial data. - Select "categoryid=sports" from the Search Assistant list.
- Press Enter, or click the Search icon on the right side of the Search bar, to run the search.
Matching Searches
The Search Assistant likewise returns matching searches, which are based on the searches that you take recently run. The Matching Searches listing is useful when you want to run the same search from yesterday, or a week ago. Your search history is retained when you log out.
The Search Assistant is more useful after yous start learning the search language. When you type search commands, the Search Assistant displays command information.
Retrieve events from the index
Permit'southward try to find out how many errors have occurred on the Buttercup Games website.
To retrieve events that mention errors or failures, you lot type the keywords in your search criteria. If you employ multiple keywords, you must specify Boolean operators such as AND, OR, and NOT.
The AND operator is implied when you type in multiple keywords.
For example, typing buttercupgames error is the aforementioned equally typing buttercupgames AND fault .
- Start a new search.
- Change the time range to All time.
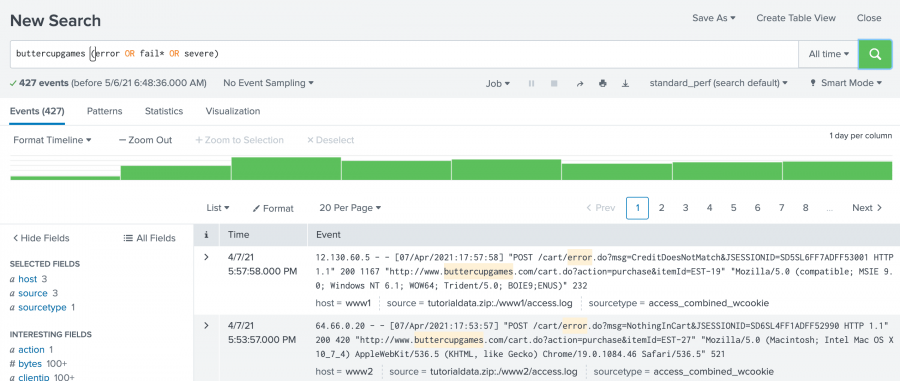
- To search for the terms error, neglect, failure, failed, or severe, in the events that also mention buttercupgames, run the following search.
buttercupgames (fault OR fail* OR severe)Tip: Instead of typing the search string, you can copy and paste the search from this tutorial directly into the Search bar.
- Click the Search icon to the right of the fourth dimension range picker to run the search.
Detect that you must capitalize Boolean operators. The asterisk ( * ) character is used as a wildcard character to match neglect, failure, failed, failing, and then along.
When evaluating Boolean expressions, precedence is given to terms within parentheses. NOT clauses are evaluated before OR clauses. AND clauses accept the lowest precedence.
This search retrieves 427 matching events.
Understanding search results
Below the Search bar are four tabs: Events, Patterns, Statistics, and Visualization.
The type of search commands that you lot employ determines which tab the search results appear on. In the early parts of this tutorial, you lot volition work with the Events tab. Later in this tutorial, you lot will learn well-nigh the other tabs.
The Events tab displays the Timeline of events, the Brandish options, the Fields sidebar, and the Events viewer.
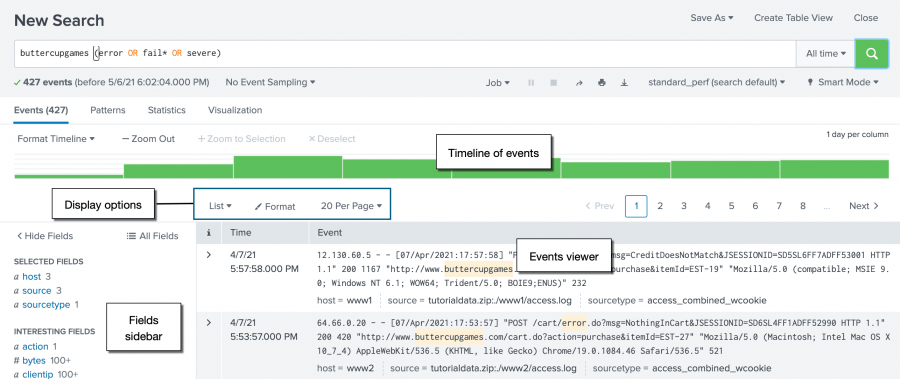
By default, the events appear as a list that is ordered starting with the most recent event. In each event, the matching search terms are highlighted. The List display pick shows the event information in 3 columns.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| i | Use the event information cavalcade to expand or collapse the display of the outcome information. By default the brandish is complanate. Click the greater than ( > ) symbol to aggrandize the display. |
| Time | The timestamp for the event. When events are indexed, the timestamp in the outcome is extracted. If the event does non contain a timestamp, the indexing process adds a timestamp that is the date and time the effect was indexed. |
| Upshot | The raw event information. The Selected fields from the Fields sidebar appear at the bottom of each event. |
Change the display of the Events viewer
- Select the List choice and click Tabular array.
The display changes to evidence the result data cavalcade, the timestamp column, and columns for each of the Selected fields. You will larn more near the Selected fields later in the tutorial. - Change the display dorsum to Listing.
Timeline of events
The Timeline of events is a visual representation of the number of events that occur at each bespeak in time. As the timeline updates with your search results, there are clusters or patterns of bars. The height of each bar indicates the count of events. Peaks or valleys in the timeline can indicate spikes in activity or server reanimation. The timeline highlights patterns of events, or peaks and lows in event activity. The timeline options are located in a higher place the timeline. Y'all can zoom in, zoom out, and change the scale of the timeline chart.
When you add data to the Splunk platform the data is indexed. Equally part of the alphabetize procedure, information is extracted from your data and formatted every bit proper name and value pairs, called fields. When you lot run a search, the fields are identified and listed in the Fields sidebar next to your search results. The fields are divided into two categories.
- Selected fields are visible in your search results. Past default, host, source, and sourcetype announced. Yous can select other fields to bear witness in your events.
- Interesting fields are other fields that have been extracted from the events in your search results.
You can hide the fields sidebar to maximize the results area.
Patterns, Statistics, and Visualizations
The Patterns tab displays a list of the virtually common patterns among the prepare of events returned by your search. Each of these patterns represents events that share a similar structure.
The Statistics tab populates when y'all run a search with transforming commands such equally stats, top, chart, and so on. The keyword search for "buttercupgames" does not show results in this tab because the search does not include whatsoever transforming commands.
Searches with transforming commands also populate the Visualization tab. The results area of the Visualizations tab includes a chart and the statistics tabular array that is used to generate the chart.
You lot will acquire about transforming commands, and apply the Statistics and Visualizations tabs, later in the tutorial.
Next step
Learn to use fields to search your data.
See also
- Help edifice searches using the Search Assistant in the Search Manual
- Identify event patterns with the Patterns tab in the Search Transmission
- Introduction to Pivot in the Pivot Transmission
Source: https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/SearchTutorial/Startsearching
0 Response to "When a Search Returns __________, You Can View the Results as a List."
Post a Comment